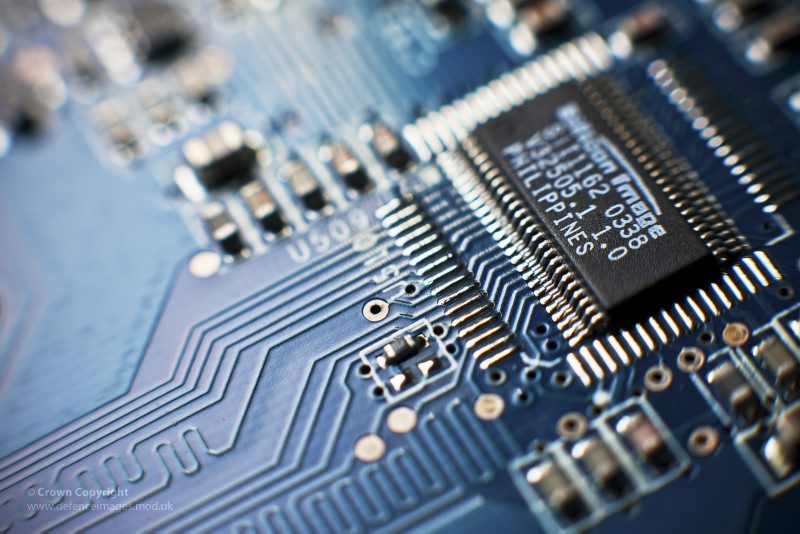
Circuit boards, the heart and brain of every electronic device, represent a perfect blend of art and science. These compact, meticulously designed components are crucial for the digital and analog functions that power our modern world. From the simplest gadgets to the most complex computing systems, circuit boards facilitate the seamless interaction of various electronic components.
This article takes you on a journey through the world of circuit boards, unveiling the beauty behind their complex pathways and the ingenious science that makes it all possible.
The Essence of Circuit Boards
How do circuit boards work? At their core, circuit boards, or printed circuit boards (PCBs), are the platforms upon which electronic components are mounted and interconnected. These boards are crafted from non-conductive materials, like fiberglass or plastic, coated with conductive pathways or traces made from copper. Each board is a masterpiece, designed with precision to route electrical signals through electronic components in a predetermined manner, fulfilling specific functions.
The Artistic Side of PCB Design
Designing a circuit board is akin to creating a piece of art. It requires not only a deep understanding of electronic principles but also a creative mind to optimize space and efficiency. The layout of a circuit board resembles a complex maze, with each line and component strategically placed to minimize noise, interference, and power consumption. The aesthetic appeal of a well-designed PCB, with its intricate patterns of traces and neatly arranged components, often goes unnoticed, hidden within the device it powers. Yet, to those who create and understand them, these boards are breathtakingly beautiful, reflecting the careful thought and creativity that went into their design.
The Science Behind Circuit Boards
The creation of a circuit board is a feat of engineering that involves several scientific disciplines, including chemistry, physics, and electrical engineering. The process begins with the schematic design, where circuit designers use software to layout the circuit, defining the electrical connections between components. This schematic is then translated into a physical design, indicating the placement of components and the routing of traces on the board.
Materials science plays a crucial role in the selection of substrates and conductive materials, balancing factors such as thermal stability, conductivity, and cost. The manufacturing process involves techniques such as photolithography, etching, and electroplating, each step requiring precise control to ensure the integrity of the final product.
Types and Technologies of Circuit Boards
Circuit boards come in various forms, each tailored to specific applications:
- Single-Sided PCBs: These have all components and conductive traces on one side of the board, suitable for simple electronics.
- Double-Sided PCBs: With components and traces on both sides, these boards offer more complexity in a compact form.
- Multilayer PCBs: Featuring several layers of conductive traces separated by insulating materials, multilayer PCBs are used in sophisticated, high-performance devices.
- Flexible PCBs: Made from flexible materials, these PCBs can bend, allowing them to fit into unconventional spaces and moving parts.
- Rigid-Flex PCBs: Combining the best of rigid and flexible PCBs, these offer versatility for complex electronic assemblies.
Innovations in PCB technology continue to push the boundaries, with advancements in materials, miniaturization, and manufacturing techniques making circuit boards more efficient, durable, and capable than ever before.
Circuit Boards in Everyday Life
The ubiquity of circuit boards in modern life cannot be overstated. They are in everything from consumer electronics like smartphones and laptops to critical applications in healthcare, automotive, and aerospace industries. The functionality and reliability of these devices depend heavily on the design and quality of their circuit boards, making them indispensable in our digital age.
The Future of Circuit Board Technology
As technology advances, the future of circuit boards looks promising, with trends pointing towards even greater miniaturization, flexibility, and integration. Emerging technologies like wearable devices and the Internet of Things (IoT) demand innovative PCB solutions that are small, energy-efficient, and capable of seamless communication.
Sustainability is also becoming a significant consideration, with the industry exploring eco-friendly materials and recycling methods to minimize the environmental impact of discarded electronics. The development of organic and biodegradable PCBs is an exciting area of research that could redefine the future of electronic devices.
Conclusion
Circuit boards, the wired wonders behind our electronic devices, epitomize the harmonious blend of art and science. Their design and manufacturing require a delicate balance of creativity, precision, and scientific knowledge, making them much more than mere components. As technology continues to evolve, the importance of circuit boards and the innovations in their design and production will only grow, driving the future of electronics towards new horizons. The art and science of circuit boards remind us of the incredible ingenuity and creativity of human technology, transforming simple materials into the engines of our digital world.